Table of Contents
What is osteotomy?
Osteotomy refers to any type of surgery in which a person’s bones are broken and deformed. The surgeon may need to perform this procedure to repair the damaged joint. This procedure may also be used to shorten or lengthen the deformed bone, which is not well aligned with the joint.
The term osteotomy is derived from the Greek. In medical dictionary, it is defined as surgery in which a bone is broken or part of a bone is removed to correct abnormalities. This article deals with the technique of cutting bone surgery in rhinoplasty.
Tips before osteotomy surgery
Each patient should have a thorough medical history and physical examination before osteotomy. The following tests should be performed:
- Complete blood cell count
- Urinalysis
- Electrolyte
- Electrocardiogram (mandatory for men over 40 and for women over 50 , If you have a history of high blood pressure, stroke, arthritis, diabetes, smoking, or any other medical reason, you may need an electrocardiogram at any age.)
- Pregnancy test in women of childbearing age
- Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) diagnosis test, hepatitis B and hepatitis C test

Imaging before surgery
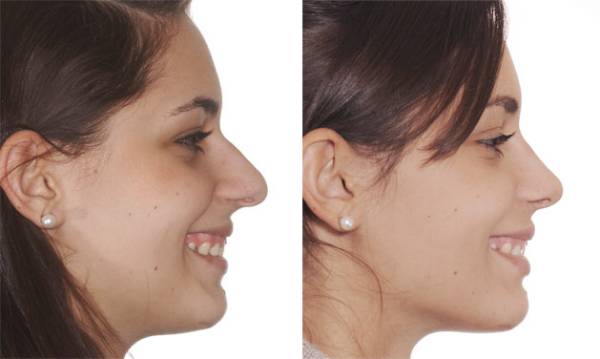
Imaging before surgery is essential for the patient. These images are examined before surgery to discuss what the patient is unhappy about. These days, digital photography has become very popular with computer programs that allow patients to see the results of possible surgery.
Types of osteotomy in rhinoplasty include:
Lateral and lateral osteotomy – This procedure is performed along the front of the upper jaw and in some cases extends to the nasal bone.
- Intermediate osteotomy – This procedure is performed to ensure the occurrence of fracture lines according to the surgeon’s wishes. This procedure may be used if it is difficult to damage with lateral osteotomy.
Upper osteotomy – This procedure may be performed if the nasal bones are unusually thick and there is a concern about an unwanted fracture line connecting the lateral and internal fracture lines.
Types of osteotomy in rhinoplasty include:
- Lateral osteotomy – This procedure is performed along the front of the upper jaw and in some cases extends to the nasal bone.
- Middle osteotomy – This procedure is performed to ensure that the occurrence of fracture lines according to the surgeon’s desire. This procedure may be used if it is difficult to damage with lateral osteotomy.
- Upper osteotomy – This procedure may be performed that the nasal bones are unusually thick and there is a concern about an unwanted fracture line connecting the lateral and internal fracture lines.
The cause of osteotomy
Most rhinoplasties requires some form of osteotomy, because most standard rhinoplasties require the movement or changing of the bony cartilaginous arch of the nose, which includes big parts of nose.
Epidemiology
In 2018, more than 213,000 Rhinoplasties were performed in the United States, according to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). For each of these surgeries, 4-2 osteotomies may have been performed.
Why Nasal Osteotomy?
This type of surgery is suitable for bony noses because it is used to remove, cut and correct bones. The following problems and complications can be repaired using osteotomy.
.
- Nose deviation. In cases of nasal deviation, to correct this deviation, it is necessary to break the nasal bone so that the deviation can be corrected. If osteotomy is used, the nasal bone is cut so that it is flat. Osteotomy is also used if the deviation is due to a broken or bruised nose.
- Solve the problem of wide noses. The board nasal bridge that is too wide to be seen from the front. This problem occurs when the nasal bone is too thick and can be removed with an osteotomy. In this procedure, the nasal bone is first broken and placed in such a way that the distance between the right and left sides of the nose is reduced, and as a result, the nose becomes narrower.
- Noses with hump and bulge. Another procedure used for rhinoplasty is removal of the protrusion or hump of the nose. In routine surgery, after removing the protrusion of the nose, the bridge becomes flat and the front view is sunken. But with osteotomy, the bones also come closer together after the bulge is removed, and as a result, the nose retains its natural shape after surgery.
- Nose breaking. In addition to its effect on the appearance of the nose, nasal fractures can cause other problems in people, including respiratory problems. To repair a fracture, surgeons usually use a controlled osteotomy to break the nasal bones in a controlled manner and then place it in itself place in addition for resolving the functional problems of the nose, aesthetic appearance is achieved. In this surgery, the nose is fixed with a splint or nasal plaster after the operation to strengthen the bones in place.
- Nasal anatomy. Simply , the nose is a structure made up of a frame of bone and cartilage with thin skin. The size, shape, thickness, texture, and position of the different parts of the nose depend on determining the appearance and function of the nose. The bony part is called the “bony arch.” Surgeons who perform rhinoplasty have a thorough understanding of nasal anatomy.
Details during the operation
Osteotomy is generally the last step in rhinoplasty because osteotomy can lead to significant bleeding. If an osteotomy is performed at the end of the operation, the surgeon can close the incisions quickly and place the dressing it. In this way, the surgeon uses dressing pressure to help stop the bleeding. Performing an osteotomy at the end of the rhinoplasty also causes less swelling after the operation.
Lateral osteotomy is performed along the front of the upper jaw and sometimes extends to the nasal bone. Before osteotomy, the areas where the osteotomy is to be performed are anesthetized with local anesthesia. This helps reduce postoperative pain and bleeding.
- The surgeon uses a osteotomy (the surgeon may use a guided osteotomy because it provides a better position of the nasal wall), first creating a fracture line in the piriform opening and extending to the point where the maxilla It attaches to the frontal bone
- After doing this on both sides, from the pressure of the hand can be used to move the bones, so a narrow base is created and by removing the hump, the roof of the nose is closed.
- If the nasal bone is thick or difficult to break, it may be necessary to have a middle or upper osteotomy.
- Lateral osteotomy may be performed subcutaneously, not through the Piriform diaphragm. Using an osteotomy, several holes may be made along the proposed fracture line of the nose. Once again, hand pressure is needed to move the bones. This creates a narrower base.
- Middle osteotomy is performed to ensure that the fracture lines are created according to the surgeon’s opinion. A small osteotomy runs along the nasal septum to the frontal bone of the nose, so the nasal bone is released and it is easier to move.
Upper osteotomy may also be performed when the nasal bones are unusually thick and there is concern about an undesired fracture line connecting the lateral and medial fracture lines. Direct subcutaneous piercing using a small osteotomy makes it possible to create an upper fracture line. In this case, the bones are moved again by hand pressure.
After the end of the osteomyelitis and the displacement of the nasal bones, all the incisions should be closed quickly. After reconstructing the bone structures, a nasal splint is used to prevent the bones from moving.
Recommendations after osteotomy surgery
The splint should remain in place for about a week for the fracture to heal. No dressing is needed after the splint has been removed.
A person can expect a small amount of bleeding from the nose that stops 12 to 24 hours after surgery. Bruising and swelling may also form around the eyes and nose due to osteomyelitis and improve after 1 to 2 weeks.
Physical activity should be limited after surgery. The patient may resume normal physical activity within a few weeks. However, because it takes about 6 weeks for a bone to heal and therefore the fracture lines may be weak for some time, certain physical activities (such as sprinting, horse riding, skiing) should be avoided during this time. In addition, activities that cause nasal trauma should be avoided during this time. After the bone has healed, the nasal arch should be about as resistant to fracture as it was before the operation.
After rhinoplasty, the soft tissue of the nose becomes stiff, which gradually clears up in about 1 year. The appearance of the nose comes close to normal after a few months, and usually changes slightly with a slight firmness of the final tissue.